Walk into any supplement store and you’re likely to be overwhelmed. Labels with mysterious words like citrulline, arginine, and nitrate promise everything from improved exercise performance and energy levels to boosting testosterone. In most cases, these pre-workout supplements are a great help and will improve your body’s ability to exercise.
Pre-workout supplements generally don’t have harmful side effects when you take the proper dose, but it’s always wisest to get medical advice from a trusted doctor before you start taking pre-workout supplements.
Anyone unfamiliar with or curious about the effects of the most popular pre-workout supplements can read through this guide to find out all the basics.
(Note: Want our elite trainers to help you make the most of your pre-workout? Start your Fitplan free trial today!)
What Are Pre-Workout Supplements?
The word supplement is an umbrella term for nutrients that the body either can’t make itself or benefits from having in large quantities. They’re most commonly sold in powders that can be mixed with water or milk but they can also come in pill, bar, liquid, or meal form.
You can take supplements before, during, and after a workout. Pre-workout and supplements meant to be consumed in the middle of a routine are fairly similar in that they give your body more fuel. Post-workout supplements are generally geared toward giving your body protein and other things it needs to rebuild muscle.
We haven’t found the pre-workout supplement yet that can turn you into the hulk so you can lift 400 pounds above your head. Nonetheless, supplements can give your body that edge to power through a workout and prepare it for muscle recovery after you finish.
(Note: You can download the Fitplan App for free on Google Play!)
Common Pre-Workout Supplements
The most popular pre-workout supplements are creatine, taurine, BCAAs, and B vitamins. Arginine and citrulline are also favored boosters of nitric oxide, a chemical compound to dilate your blood vessels and increase blood flow, lowering your blood pressure and flooding muscle tissue with more blood to protect them from injury.
You may also have heard of whey protein supplements, and while they are very popular, they work best to stimulate protein synthesis and repair muscle tissue post-workout.
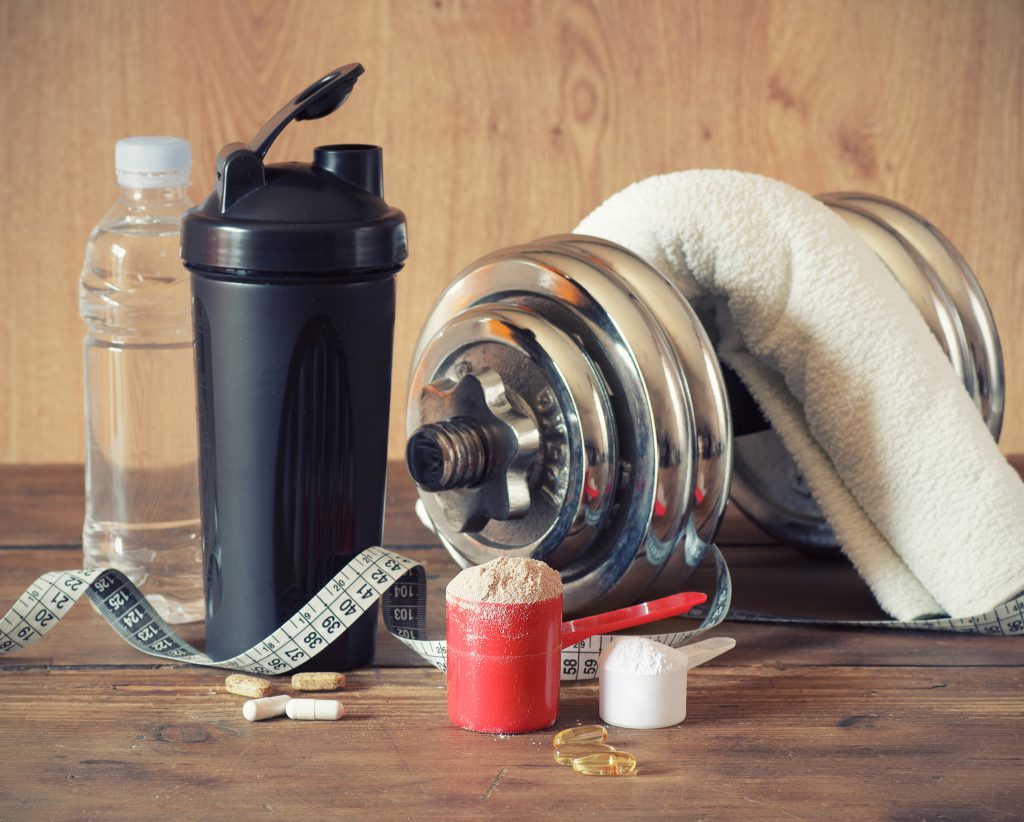

What’s in Pre-Workout Supplements?
Many multi-ingredient pre-workout formulas include additives like sugar alcohols for flavor and caffeine to boost energy levels during a high-intensity workout. Generally speaking, they have as much caffeine as a cup of coffee and their sugar content is still less than a typical energy drink. But make sure you read the label and know exactly what’s inside because the contents of proprietary blends can vary.
Some manufacturers use a caffeine alternative called methylhexanamine or DMAA, which although effective to boost energy comes with a warning from the FDA that it might cause heightened blood pressure or even heart attacks.
Creatine is frequently added to multi-ingredient blends even if it isn’t the main ingredient. It’s made naturally in your kidneys but having more of it will help your body make more protein and boost energy levels. Taurine has similar effects on increasing hypertrophy and helping with muscle recovery.
Helpful Hint: A creatine-rich supplement before our Train Smart Fitplan will bulk up your muscle mass!
Proteins, Amino Acids & Pre-Workout Supplements
To build muscle, you have to have protein. Your body breaks down proteins into peptides, which are short chains of amino acids used to patch muscle fibers when they’re torn during exercise.
Some pre-workout supplements have tons of protein in them, which is great for recovery and building muscle. Others have amino acids instead, leapfrogging the breakdown stage and allowing your body to put the peptides to good use sooner.
The most important thing you need to know about amino acids is that there are 20 in total and, of those 20, there are 9 essential amino acids that your body cannot make itself and so must find in food sources. Food sources that have all 9 essential amino acids, such as dairy, eggs, meat, and poultry, are called complete proteins.
Whey protein powder for your post-workout replenishment is a complete protein while creatine contains three: glycine, arginine, and methionine. These three amino acids are converted and stored in muscles for energy, which is why creatine is such a popular pre-workout supplement.
Branched-chain amino acids, or BCAAs, are three essential amino acids with a particular structure. Valine, leucine, and isoleucine are their names.
Leucine promotes protein synthesis, which is the process by which your body creates new muscle. The three BCAAs have also been shown to delay exercise fatigue and decrease muscle soreness when consumed about 1 hour before a workout.
While BCAAs and all the other essential amino acids can be found in complete protein foods and supplements, some bodybuilders prefer to take additional BCAAs to boost muscle growth and maintain energy.
Benefits & Side Effects of 7 Popular Pre-Workout Supplements
Almost everything people use for supplementation seems to have the same benefit: it either builds muscle, makes you stronger, or gives you energy. A closer look at these supplements will give you a better idea of their specific purposes and how you can use them most effectively.
1. Creatine
Benefits: Creatine boosts exercise performance because it leads to the creation of adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, which your body stores in its muscles to use for energy during exercise. When there’s more creatine in your system, your body can create more ATP and power through workouts more effectively.
Creatine also draws water into your muscles and makes them appear larger in addition to helping them function better. Better signaling between the cells that help rebuild muscle and increased production of growth hormones from creatine also helps your muscles grow.
For many people, creatine is the beginning and end of their supplementation regimen.
Possible Side Effects: There hasn’t been much research on the long-term effects of creatine. Some researchers say creatine supplementation has no adverse effects for healthy individuals while others claim it can damage the kidneys if taken for too long.
Although harmless, muscle cramps are also a common side effect of creatine. Occasional temporary side effects of creatine could include dehydration and bloating. You’ll more than likely be just fine taking it at the right dosage, though.
Helpful Hint: Put your creatine supplement to the test with our Power Shred Fitplan!
2. Beta-Alanine
Benefits: To understand what Beta-Alanine does, you have to first understand how lactic acid buildup affects your muscles. During exercise, your muscles consume glycogen for energy. Glycogen becomes lactic acid, which interferes with glucose breakdown and prevents your muscles from getting more energy.
Beta-Alanine prevents this interaction by combining with an amino acid called histidine to form carnosine, which reduces muscle acidity, allowing glucose breakdown to continue. In short, beta-alanine will stave off muscle fatigue during high-intensity workouts.
Possible Side Effects: Taking too much beta-alanine can cause paraesthesia, a harmless tingling sensation on your skin. Stick to lower doses of around 1.6 g and you should be able to avoid this side effect.
3. BCAAs
Benefits: Branched-chain amino acids help reduce muscle soreness and delay fatigue during high-intensity workouts. One important thing to note is that you can get BCAAs through whole proteins like poultry, eggs, and meat. It will be absorbed more slowly by your body. If you want a pre-workout boost, though, BCAA supplementation will do the trick.
Leucine, one of the BCAAs, helps promote protein synthesis, which will help build muscle mass after the workout is finished. There’s no evidence that BCAAs help your physical performance, but they can keep your muscles working longer and the supplemental variety is fast-acting because it is taken up directly by your muscles rather than getting processed in your liver first.
Possible Side Effects: For most people, consuming BCAAs won’t have any severe side effects. Occasional nausea, headaches, and minor soreness could occur. Get medical advice from your doctor if you’re taking prescribed medication because BCAAs may interfere with certain kinds.
4. Citrulline (AKA L-Citrulline)
Benefits: The main effect of citrulline is a widening of veins and arteries, allowing for better blood circulation and lower blood pressure. Unlike many of the other dietary supplements on this list, citrulline isn’t used to build proteins, but it can still help promote protein synthesis by stimulating an important signaling pathway.
Citrulline also improves muscle oxygen use, making them more efficient during exercise. It also reduces muscle soreness in the days following high-intensity workouts. Citrulline is commonly mixed with a workout ingredient called malate that helps boost energy.
Possible Side Effects: No negative effects of citrulline have been reported, even at high dosages. Your body isn’t able to process citrulline after a certain amount of arginine saturation in your blood, so measuring out the right dosage can help you use your supply of citrulline more effectively and preserve your supply for a longer time.
5. L-Arginine
Benefits: While it can be produced from citrulline, L-arginine is also readily available in common protein-rich foods and as a standalone dietary supplement. It is needed to produce nitric oxide, which works similarly to citrulline in terms of improving muscle oxygenation and blood flow.
L-arginine also helps boost insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, both of which help your body convert the glucose from carbs into glycogen to store in your muscles and use for energy during a workout.
Possible Side Effects: In large doses, L-arginine has been reported to cause nausea, diarrhea, bloating, and abdominal pain. At regular doses of several grams a day, these symptoms are very uncommon. Some conditions negatively impact how your body processes arginine, so if you want to take it as a dietary supplement for a long period, consult your doctor.
6. B Vitamins
Benefits: The three B vitamins, including vitamin B-6, riboflavin, thiamin, folate, and vitamin B-12, are important for building red blood cells and helping convert carbohydrates and proteins into energy. High-intensity exercise increases your body’s need for B vitamins. The red blood cells B vitamins build help transport oxygen and rebuild damaged muscle.
While lifters who have a balanced diet likely get enough B vitamins from their diet, people eating no or limited carbs as part of a diet or cutting phase can benefit greatly from taking a B vitamin dietary supplement.
Possible Side Effects: Some B vitamins like B6 and B3 can cause a loss of appetite, stomach discomfort, vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, headaches, and drowsiness. To get these symptoms you have to overtake B vitamins to a point of toxicity. Your body will generally expel excess B vitamins through your urine.
Helpful Hint: Get long-term results with our 21-Day Workout Series Fitplan!
7. Caffeine
Benefits: For seasoned weightlifters, caffeine can boost athletic performance and lifting power. This boost is more visible in compound exercises that use large numbers of bigger muscles than with isolated exercises and small muscle workouts. Caffeine can also help your body burn more fat during a workout, so it can help during a cutting period that aims to shed a few pounds of body fat.
Be aware that many proprietary blends and multi-ingredient dietary supplements contain caffeine in them already. If you want to supplement with caffeine on its own, make sure your other supplements don’t have lots of caffeine already or you could experience some bad side effects.
Possible Side Effects: We all know about the jitters you get when you have one cup of coffee too many. That’s because the caffeine in a cup of coffee works as a nervous system stimulant. Similarly, caffeine taken as a dietary supplement can also lead to increased heart rate, irritability, sleeplessness, anxiety, shaky hands, and stomach pain.

Common Pre-Workout Supplementation Mistakes
Many of these pre-workout supplements help achieve fitness and sports nutrition goals as well as general wellness. However, you might wreck their effectiveness if you commit one of these common mistakes:
Replacing Meals with Supplementation
Although these supplements have significant benefits to lifters, they aren’t as well-rounded as complete proteins and the macronutrients you need for your body to work at its most optimal level. Cutting phases can make us do some crazy things like skipping entire meals in place of supplements and protein shakes, but you’re only depriving your body of the nutrients it needs if you do so.
Remember that these supplements are meant to work in tandem with many, many other nutrients. They are called dietary supplements, after all – they’re supposed to supplement a healthy, balanced diet. Even though science has given us these helpful substances in pill, liquid, and powder form, nothing beats our digestive system for getting the majority of the nutrients our bodies need.
Timing Your Intake Incorrectly
There’s a reason some supplements are considered pre-workout while others are post-workout or meant to be consumed in the middle of the session. Your body digests and processes each one differently. That’s why some people prefer BCAA supplementation rather than getting all their branched-chain amino acids from their diet – the supplemental variety is processed and put into action much quicker.
Other people use the supplements correctly but take them too early or too late for them to take effect during their workout routine. Most pre-packaged supplements will have instructions on the label for how much to take and when. Some need to be taken 30 minutes to 1 hour before a workout while others have a slower release and might need to be taken earlier.
Over-Consumption
Even if it doesn’t lead to nasty side effects, taking too much pre-workout supplement is a waste of time and money. Your body can only process so many nutrients in a given time and it will usually pass the rest out through waste. These dietary supplements are going to seem much more expensive than they are if you’re wasting part of them by taking too much.
In some cases, people take the right amount but take supplements too many times in a day. This is effectively the same as over-consumption in one sitting and may cause digestive trouble, nervousness, headaches, or a jittery feeling depending on which supplement you’re taking too much of.
Not Enough Research
Big mixes can have tons of added ingredients like carbohydrates and sugars. In most cases, they aren’t in the mix in large enough quantities to completely ruin a diet or a cut. But if you’re consuming too much pre-workout, you could easily be giving your body way more carbs and sugar than you think, ruining your macro count.
The most reputable brands have all their contents listed on the label and have been examined by some certification body. It never hurts to hit the internet and look for information on the specific supplement by brand name because proprietary blends can have way different ingredients depending on who makes them.
Helpful Hint: Add our Lean Theory Fitplan to your next cut to shred some serious body fat!
Conclusion
Pre-workout supplements are a great way to give your body a bit more of the nutrients it needs to power through a workout and improve your body composition in the recovery phase following a gym session. Understanding which supplements have what effects and how you can best fit them into your fitness plan will help prevent some annoying and potentially harmful side effects.
Just remember that these aren’t magical concoctions. In many cases, they’re naturally occurring in food or already produced by your body. Getting nutrients in higher concentrations with pre-workout supplements can help your body perform better and build better muscle, though, as long as you take them at the right time and in the right amount.
(Note: Want our celebrity trainers to help you kickstart your fitness journey? Start your Fitplan free trial today!)